The Government of Canada has issued a new Canada Research Chair (CRC) appointment to York University Professor Godfred Boateng in global health and humanitarianism, as well as renewed the Chairs of three other faculty members – Ethel Tungohan (Faculty of Liberal Arts & Professional Studies), Isaac Smith (Lassonde School of Engineering) and Steven Connor (Faculty of Science).
The CRC program facilitates world-class research at Canadian universities, boosting their global competitiveness, while also providing training opportunities for the next generation of highly skilled personnel through research, teaching and learning.
“From global health to migration policy to planetary science to neurophysiology, York University faculty are at the forefront of research excellence in their respective fields,” said Amir Asif, vice-president research and innovation. “I extend my sincere congratulations to our four new and renewed Canada Research Chairs whose impactful work benefits the lives of both Canadians and people around the world.”
Learn more about the new and renewed chairholders at York:

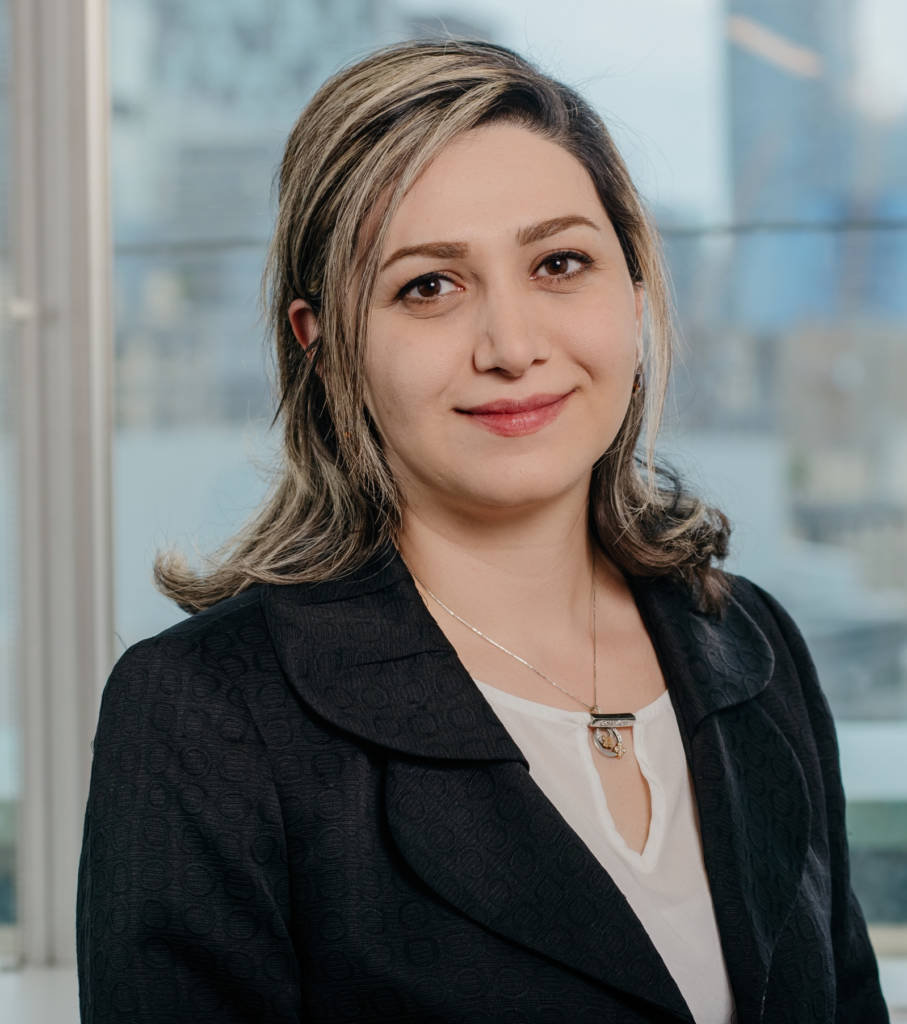
Godfred Boateng, Canada Research Chair in Global Health and Humanitarianism
Boateng is an assistant professor in the School of Global Health, director of the Global & Environmental Health Lab and a faculty fellow at the Dahdaleh Institute for Global Health Research. He is also the principal investigator on a new project called “Retooling Black Anxiety” in the Greater Toronto Area.
As a CRC, Boateng will address global health priorities by focusing on anticipatory, instead of reactionary, approaches. Notably, he will look to further understand the synergistic epidemics of food, water, energy, and housing insecurity and their compounding effects, as well as the impact of environmental degradation and changes in climatic conditions on the health of older adults in sub-Saharan Africa and Canada.

Ethel Tungohan, Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Canadian Migration Policy, Impacts and Activism
With her CRC renewal, Tungohan, an associate professor in the Department of Politics in the Faculty of Liberal Arts & Professional Studies, will build on her work assessing the interconnections between policies, everyday lived experiences and social movement organizing.
She will continue to look at the impact on migrant workers, Canadian discourse, and policies on immigration, labour, and occupational health and safety in the pre-pandemic, pandemic and post-pandemic era.

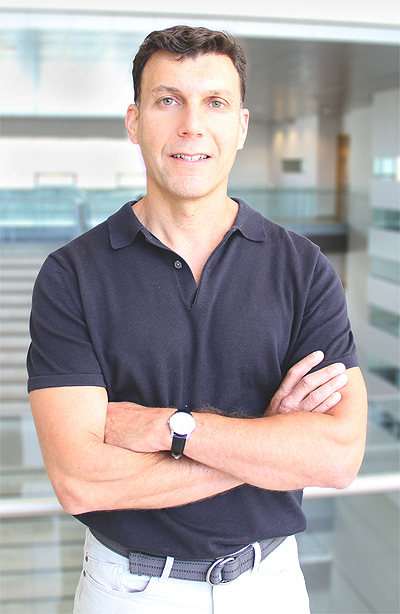
Isaac Smith, Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Planetary Science
Smith, an assistant professor in the Department of Earth & Space Science & Engineering in the Lassonde School of Engineering, will use his CRC renewal to investigate aspects of ice and climate on Mars and other parts of the solar system, including Pluto and Triton, Neptune’s moon.
The research is unique to York University and aims to advance knowledge of Mars’ climate and ice-related processes, in addition to performing glaciological modelling on icy worlds in the outer solar system.

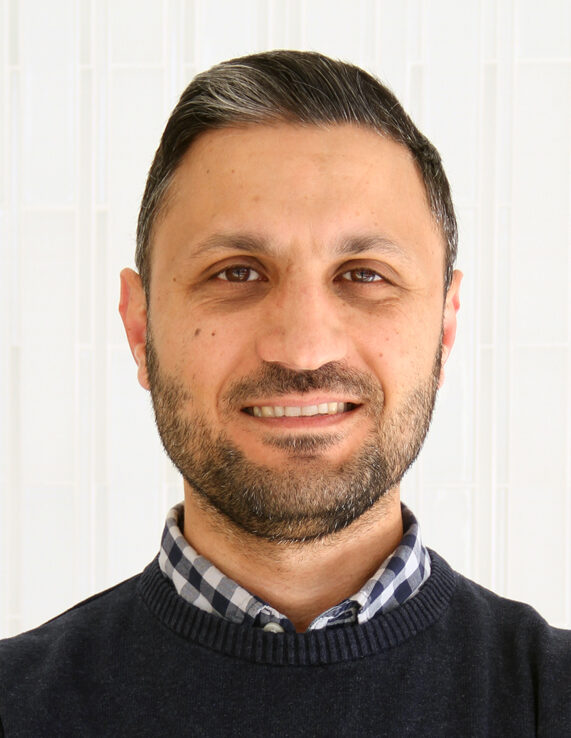
Steven Connor, Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in the Synaptic Basis of Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Connor, an assistant professor in the Department of Biology in the Faculty of Science, will use his CRC renewal to focus on investigating how specific brain proteins facilitate the transmission of information between brain cells. The research aims to further understand how those proteins influence neural circuit function and activity, and how they can result in autism-like behaviour when compromised. Connor and his research team will also explore the restorative effects of reversing molecular changes linked to the loss of certain brain cells.