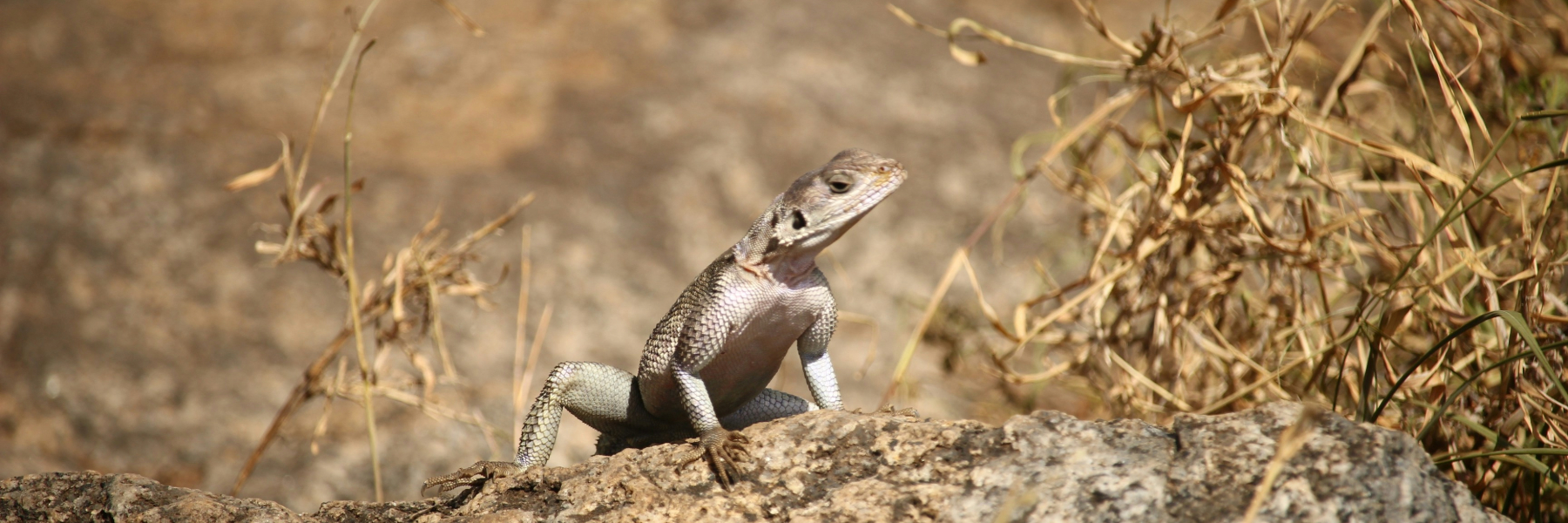
Mario Zuliani, a York University researcher and teaching assistant in the Faculty of Science, is making inroads in the field of ecology with his novel study on the association between imitation plants and animal species.
Expected to complete his PhD at York in August, Zuliani has already made significant contributions to ecological science, including a recently published paper in Restoration Ecology titled “The Relative Effects of Artificial Shrubs on Animal Community Assembly.”
Zuliani’s environmental research took root during his master’s program in biology at York, where from 2018 to 2020 he focused on ecological conservation and restoration, particularly through studying the relationship between shrubs and animal species. Building on this earlier work, Zuliani’s latest study digs deeper into the facilitative interactions between shrub and animal species, exploring how structures that mimic shrubs might be utilized by animal species in the wild.
Explaining the motivation behind his research, Zuliani highlights the importance of shrub species in arid ecosystems such as those found in Southern California. These shrubs play a crucial role in providing shelter, food and protection for a diverse range of animal species, mitigating the harsh conditions of the desert environment.
Fake shrubs serve much of the same purpose, Zuliani and his team have found, providing compelling evidence that artificial shrub structures can replicate the benefits of natural shrubs, attracting similar animal communities and providing essential resources for survival.
“From our study, we found that artificial shrubs can produce the same benefits that natural shrubs produce. They reduce the temperature under their canopy and even have the same animal species associating around them,” Zuliani says. “We also found that animals prefer being closer to either artificial shrubs or natural shrubs, rather than in areas where there are no shrubs. This is important because it shows that these artificial structures will be used as a resource by animals.”
The implications of Zuliani’s research are far-reaching, offering valuable insights for conservation and restoration efforts in disturbed ecosystems.
“One of the biggest actions I am hoping to come about from these findings is the use of artificial shrubs as a short-term solution to promote animal communities in areas where natural shrubs have been disturbed, or in areas where there are endangered animal species,” he says. “Finding that these dry-land animal species utilize these artificial shrubs suggests that they can be used, at least for a short time, while natural shrubs are able to grow in size and provide the same benefits.”
By demonstrating the effectiveness of artificial shrubs as a temporary solution to promote animal communities, Zuliani also hopes to pave the way for sustainable initiatives that support endangered species and mitigate the impacts of habitat loss and climate change.
“Utilizing artificial shrubs – and by extension artificial structures – could have positive impacts on sustainability initiatives, as they can all be used temporarily while disrupted ecosystems recover,” Zuliani says. “As well, using these types of structures, even for just a short period of time, would relieve stress that animals experience when they have lost habitats or when their environment has become increasingly harsh from global climate extremes.”