By Elaine Smith
While working toward a master’s degree in health equity, Erin Flanagan’s experiential education (EE) opportunity in the Human Rights & Health Equity graduate course offered by Jessica Vorstermans was a factor in her decision to pursue her passion for health policy and equity in the PhD program at York University.
In addition to teaching relevant theory, Vorstermans, an assistant professor of critical disability studies, requires students in her course to engage with small organizations that are doing grassroots work. She also brings in speakers from such organizations to share their work experiences with the class.

“I want the students to engage with the people doing that work on the ground and understand what that looks like,” said Vorstermans. “We talk about community engagement in research and intersectionality, and I think it’s important for students to experience that and have time to think, reflect and debrief as part of their academic training, since they’ll likely be working in policy and different systems of care.
“The idea is for them to be close to the people who are experiencing the policies, theories and concepts my students are learning about: those who experience inequity.”
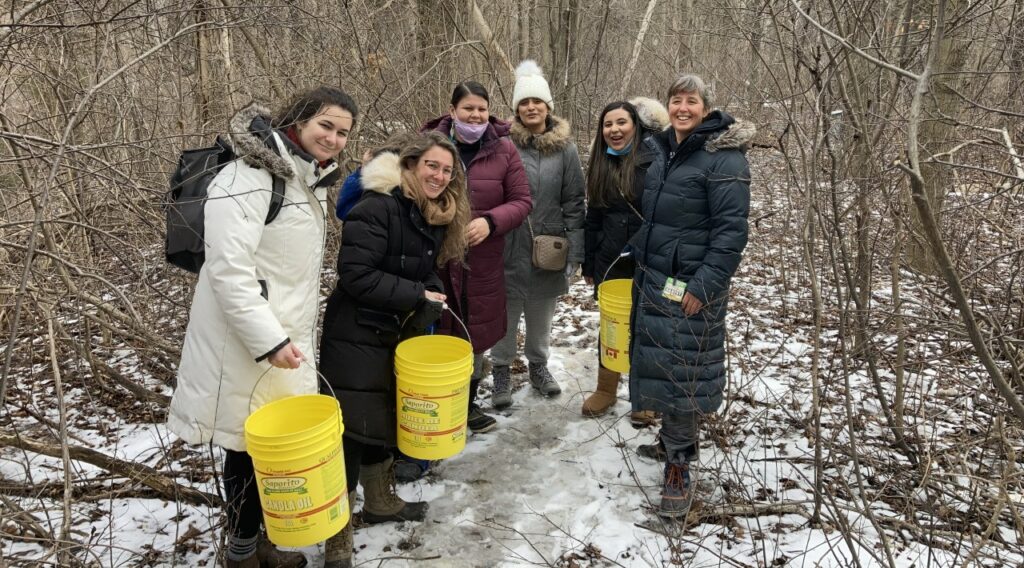
The organizations that provide Vorstermans’ students an opportunity for EE include: the Sweetgrass Roots Collective, an Indigenous collective that works to re-indigenize urban spaces, doing land- and place-based education, earthwork, arts and storytelling, to plant and steward land at Black Creek Community Farm, which is next door to York’s Keele Campus; Community Peacemaker Teams, an advocacy organization that describes itself as building partnerships to transform violence and aggression; and the Ocama Collective, “a community-directed group of birth workers of colour, living and working in Tkaronto [Toronto], who are dedicated to the reclamation of traditional and holistic childbearing and birthing practices amongst IBPIC folx” (sic).
“Learning from people experientially is powerful,” said Vorstermans, and both Flanagan and recent student Humairaa Karodia agree.

“The group project was the highlight of the course, because it allowed me to immerse myself into the real world,” said Flanagan. “We were doing research with a purpose, so we could see it come to fruition, see the end result and see that it made an impact.”
Flanagan and the four other students on her team worked with the Indigenous Wet’suwet’en people of British Columbia who have been protesting plans made by large corporations to build pipelines on their lands – projects that don’t have the tribe’s consent.
“We worked as an ally to support the Indigenous community with their protest, document it and ensure it got proper coverage in the media,” said Flanagan. “We provided the story from the perspective of the Indigenous community and we helped gather information so we could support the protest, researching the amount of money the RCMP was spending on the protest, including blockades and arrests of Indigenous people. We tried to find numbers so we could provide a clear look at how much public money goes into this.
“There were a lot of nuances, and we filed a freedom of information request, going through that whole process. We built skills around how to find information people try to conceal. It brought to light what is transparent and what is not.”
Their experience also caused team members to consider their own privilege, something they all discussed.
“We talked about how to form a genuine allyship and avoid tropes of the white saviour,” she said. “It helped us stay grounded. We were constantly asking questions, since we had no lived experience with the issue.”

Karodia, a master’s student in health policy and equity, chose to work with the Sweetgrass Roots Collective to harvest sweet water because she remembers childhood trips to maple syrup farms and was also eager to give back to the Indigenous community during a time of reconciliation.
“This was deconstructing what I knew about maple syrup,” she said, referring to sweet water, also known as sap. “And after all the years of hurt inflicted on the Indigenous Peoples, they still welcome settlers with open arms, asking us to come learn from them and join them. Forming these spaces allows us to see the common ground we all hold. Under the scope of human rights, this type of bonding, trust, and collaboration humanizes one another and we begin to feel like we are one body and obliged to protect one another.”
Karodia found many similarities between Indigenous Peoples and Muslims in Canada, including adherence to a lunar calendar and promoting gratitude and sustainable living.
“The way they hold their natural spaces and respect every living creature is very similar to Islam, and the West has discriminated and looked down on Islam in the same way they have on Indigenous practices and beliefs,” she said. “When we talk about agency, we think about protests and demonstrations, but bringing awareness can also be through intimate spaces like this, about bolstering your community together. Even the smallest action, such as boiling sweet water and canning it so it can go to Indigenous people throughout the province, makes a difference.”
After their EE opportunities, the teams each presented a concept they learned during their work and related it to their classroom learning. Their presentations fostered thought-provoking discussion that Flanagan found “very rewarding.”
“This practical experience was so refreshing,” she said. “It was the first time I’d done research in a group setting and the team dynamic was really enjoyable. We build some concrete skills that we could put on a resume. It was great that Professor Vorstermans offered us this opportunity.”
For her part, Vorstermans says students’ graduate work “focuses a lot on theory. When you put that together with work on the ground, you realize that things can be complicated and difficult.
“As the students move into expert mode as researchers, they need to know that their learning should be directed by those experiencing harms, injustices and oppression,” she said. “Listening is an important skill.”